人大附中早培学习资料(下篇)

接中篇
1
语文部分
考点 3:
《三国演义》中被称为“三绝”的是:奸绝曹操,智绝诸葛亮,义绝关羽。
2.《水浒传》
《水浒传》是近几年的热门考点,需要大家格外重视。
考点 1:
《水浒传》全称《忠义水浒传》,以北宋末年宋江起义的历史事实为基础创作的一部长篇章回体小说。描写了以宋江为首的 108 个好汉集聚梁山泊起义,起义后接受招安,最终失败的过程,可以将之分为三部分来掌握:108 将聚会梁山泊;受招安后征辽、田虎王庆;征方腊。第一部分是最能体现人物性格、具有众多精彩情节的部分,应该重点把握。
考点 2:
(1)天孤星花和尚鲁智深(鲁提辖、鲁达):正直无畏、见义勇为拳打镇关西——大闹五台山——火烧瓦罐寺——倒拔垂杨柳——大闹野猪
林——大闹桃花林——单打二龙山——活捉方腊——浙江圆寂(2)天雄星豹子头林冲(林教头):武艺高强、被逼为寇
结仇高衙内、误入白虎节堂——获救野猪林——棒打洪教头——风雪山神庙——雪夜上梁山.
(3)及时雨宋江(呼保义、孝义黑三郎):仗义疏财、乐于助人私放晁盖——怒啥阎婆惜——三打祝家庄(4)智多星吴用:足智多谋、屡建奇功:智取生辰纲(杨志)(5)天伤星行者武松:恩怨分明、勇武非凡
景阳冈打虎——怒杀潘金莲——大闹快活林,醉打蒋门神——血溅鸳鸯楼—
—二龙山落草(6)天杀星黑旋风李逵:率直忠诚、淳朴粗鲁
黑旋风斗浪里白条——劫法场救宋江——沂岭杀四虎为母报仇——打死殷天锡——大闹东京
考点 3:
核心人物绰号是近几年的热门考点,我们将“人物名称+绰号”制作成一张表格,有助于记忆。注意最后的三位女性。
重点人物及称号
绰号 | 人物 | 绰号 | 人物 |
呼保义 | 宋江 | 神行太保 | 戴宗 |
玉麒麟 | 卢俊义 | 黒旋风 | 李逵 |
智多星 | 吴用 | 九纹龙 | 史进 |
入云龙 | 公孙胜 | 浪里白条 | 张顺 |
豹子头 | 林冲 | 拚命三郎 | 石秀 |
小旋风 | 柴进 | 浪子 | 燕青 |
花和尚 | 鲁智深 | 一丈青 | 扈三娘 |
行者 | 武松 | 母夜叉 | 孙二娘 |
青面兽 | 杨志 | 母大虫 | 顾大嫂 |
2
英语部分
英语部分(基础数学英语词汇) :
数学 mathematics, maths(BrE), math(AmE) 公理 axiom
定理 theorem 计算 calculation 运算 operation 证明 prove
假设 hypothesis, hypotheses(pl.) 命题 proposition
算术 arithmetic
加 plus(prep.), add(v.), addition(n.) 被加数 augend, summand
加数 addend 和 sum减 minus(prep.), subtract(v.), subtraction(n.)
被减数 minuend 减数 subtrahend
差 remainder乘 times(prep.), multiply(v.), multiplication(n.)
被乘数 multiplicand, faciend
乘数 multiplicator 积 product除 divided by(prep.), divide(v.), division(n.)
被除数 dividend
除数 divisor 商 quotient等于 equals, is equal to, is equivalent to 大于 is greater than小于 is lesser than
大于等于 is equal or greater than 小于等于 is equal or lesser than
运算符 operator数字 digit 数 number
自然数 natural number 整数 integer
小数 decimal
小数点 decimal point 分数 fraction
分子 numerator 分母 denominator 比 ratio
正 positive
阅读部分
Electric cars are dirty. In fact, not only are they dirty, they might even be more dirty than their gasoline-powered cousins.
People in California love to talk about “zero-emissions(排放)vehicles”, but people in California seem to be clueless about where electricity comes from. Power plants most all use fire to make it. Apart from the few people who have their roofs covered with solar cells, we get our electricity from generators(发电机). Generators are fueled by something--usually coal, oil, but also by heat generated in nuclear power plants. There are a few wind farms and geothermal(地热) plants as well, but by far we get electricity mainly by burning something.
In other words, those "zero-emissions" cars are likely coal-burning cars. Because the coal is burned somewhere else, it looks clean. It is not true. It's as if the California Greens are covering their eyes—“If I can't see it, it's not
happening.” Gasoline is an incredibly efficient way to power a vehicle; a gallon of gas has a lot of energy in it. But when you take that gas(or another fuel)and first use it to make electricity, you waste a nice part of that energy, mostly in the form of wasted heat--at the generator, through the transmission lines, etc.
A gallon of gas may drive your car 25 miles. But the electricity you get from that gallon of gas won't get you nearly as far -- so electric cars burn more fuel than gasoline-powered ones. If our electricity came mostly from wind or geothermal, or solar, then an electric car truly would be clean. But for political, technical, and economic reasons, we don't use much of those energy sources.
In addition, electric cars' batteries which are poisonous for a long time will eventually end up in a landfill. And finally, when cars are the polluters, the pollution is spread across all the roads. When it's a power plant, though,all the junk is in one place. Nature is very good at cleaning up when things are not too concentrated, but it takes a lot longer when all the garbage is in one spot.
1:What’s the main idea of the passages?
A.Electric cars aren’t actually clean.
B.Electric cars are zero-emissions vehicles.
C.Zero-emissions vehicles are popular.
D.Gasoline-powered cars are more efficient.
2:Which of the following words can replace “be clueless about” in Paragraph 2? A.Be familiar with.
B.Be curious about.
C.Fail to understand.
D.Show their interest in.
3:The electricity we get from a gallon of gas may make our car run _________. A.at least 25 miles
B.more than 25 miles
C.as far as 25 miles
D.less than 25 miles
4:In the author’s opinion, compared with cars using gas, electric cars are more
__________.
A.environmentally-friendlyB.expensive
C.efficientD.harmful
5:It can be inferred from the passage that __________. A.electric cars' batteries are poisonous for a long time
B.now electric cars are used more than their gasoline-powered cousins
C.zero-emissions vehicles should be chosen to protect our environment
D.electric cars are not clean in that we get electricity mainly by burning something
答案小题 1:A 小题 2:C 小题 3:D 小
Mulch is a protective cover of material that is spread on top of soil. It is usually made out of organic material, like crop waste. Farmers may keep the remains of maize or other crops on top of the soil. This creates mulch on the soil surface. The plant remains help protect the soil against wind and water damage. Mulching is one of the best things people can do for their plants. It also helps keep the soil from getting dry, and reduces the need for watering plants. It also limits temperature changes in the soil. And it stops unwanted plants, or weeds,from growing. Organic mulch improves the condition of soil. As the mulch breaks down, it
provides material which keeps the soil from getting hard. This improves the growth of roots and increases the movement of water through the soil. It also improves the ability of the soil to hold water. Organic mulch contains nutrients for plants. It also provides a good environment for earthworms and other helpful organisms in the soil.
It is easy to find organic mulch materials. Cutup leaves and small pieces of tree bark can be used. Grass cuttings are also a good mulch for plants. Mulch from newspapers works well in controlling weeds.
The best time to add mulch depends on your goal. Mulch provides a thick barrier between the soil and the air. This helps to reduce temperature changes in the soil. As a result,mulched soil will be cooler than other soil in the summer. In winter, the mulched soil may not freeze as deeply as other soil. The best time is after the ground has frozen, but before the coldest weather arrives. Spreading mulch before
the ground has frozen may attract small animals searching for a warm place to spend the winter. Delaying the spreading should prevent this problem. The animals will probably find another place to live.
1:The author tells us the following EXCEPT________.
A.what mulch is and its benefits
B.the best time to add mulch
C.what can be mulched on the soil surface
D.the bad effects of mulch
2:The following can be used as organic materials to make mulch EXCEPT________.
A.tree barksB.cutup leaves
C.grass cuttingsD.plastic
3:Which of the following is the benefit of mulch?
A.Protecting the soil against wind and water damage.
B.Keeping the soil wet and reducing the need for watering plants.
C.Reducing temperature changes in the soil and stopping unwanted weeds growing.
D.All of the above.
4:The main idea of Paragraph 2 is that organic mulch can________. A.improve the condition of soil
B.improve the ability of the soil to hold water
C.provide a good environment for earthworms
D.improve the growth of roots and increase the movement of water through the
soil
5:From the last paragraph, we know ________.
A.the best time to add mulch is in spring and summer
B.the best time to add mulch is after the coldest weather arrives
C.the best time to add mulch depends on weather
D.choosing the best time to add mulch can avoid attracting small animals
3
百科部分
附件:科学百词
物理部分
1.熔化:从固体到液体的过程,吸热。
2.凝固:从液体到固体的过程,放热。
3.汽化:从液体到气体的过程,吸热。
4.液化:从气体到液体的过程,放热。
5.升华:从固体到气体的过程,吸热。
6.凝华:从气体到固体的过程,放热。
7.密度:物理量,物质单位体积内的质量。用字母ρ来表示。单位为 g/cm²。
8.热胀冷缩:多数物质具有的性质,加热后体积膨胀。其原因是组成物质的粒子距离因加热而增大。
9.压强:物体所受的压力与受力面积之比,用字母 P 表示,单位为帕斯卡 Pa。受力面积一定时,压强与压力成正比;压力一定时,受力面积与压强成反比。液体和气体压强与深度成正比。一定体积的气体,加热后压强会增大。
10.溶解度、饱和溶液:固体溶解度:一定温度和压强下,100g 水中最多可以溶解的溶质的质量。气体:气体的溶解度:一定温度和压强下,气体在 1 体积溶剂中达到饱和状态时的体积。大多数固体溶解度随温度升高而增大,气体溶解度随温度升高而降低。一定温度下,不能再继续溶解某种溶质的溶液称为饱和溶液。饱和溶液的浓度等于“溶解度÷(溶解度+100)×100%”。
11.热传导:热量传递方式之一,热能从高温向低温部分转移的过程。
12.热辐射:热量传递方式之一,物体由于具有温度而辐射电磁波的现象。
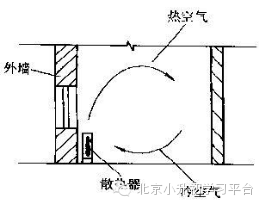
13. 热对流:热量传递方式之一,热量通过流动的介质在空间传播的现象(如上图)。
14.声波:发声体产生的振动在空气或其他物质中的传播。声波是一种机械波,需要介质,可以发生反射。
15.频率:单位时间内振动的次数。单位为赫兹 Hz。频率在 20~20000Hz 之间的声波,人耳可以听见,随着衰老,这个范围会变窄。
16.声源:发出声音的物体。振动才会发出声音。如发声的声带,演奏中的乐器,震源等。
17.介质:波的传播所依赖的物质。声波需要借助气体、液体或固体传播,成分、温度、密度都会对传播速度和方向造成影响。电磁波可以在透明的气体、液体和固体中传播,也可以在真空中传播。
18.音调:声音三要素。音调取决于频率,频率越高音调越高。
19.响度:声音三要素。响度取决于振动幅度,振幅越大响度越大,也就是声音越响亮,我们所说的分贝,就是响度的单位,分贝数越大,音量越大。
20.音色:声音三要素。音色是不同物体发出声音时其品质的区别,比如钢琴和二胡同时奏出同样高的音,我们一下就可以分辨出来,不同的人说话,也能分辨,这都是音色的区别。
21.惯性:物体保持静止或匀速直线运动的性质。不受力或受力平衡时,物体保持原来的运动状态,即静止或匀速直线运动。物质的质量越大惯性越大。
22.质量:物体所包含物质的数量。单位是 g 或 kg。地球上的重量约等于质量。
23.重力:物体由于地球吸引而受到的力,大约指向地心。可以用重力计测出。地球上重力和质量的比值是重力加速度。
地球上的重力加速度比月球大,这是因为地球的质量大,引力就大,所以重力加速度大,于是在地球上用秤称重,是月球上的数值的 6 倍左右。
24.向心力:物体由于圆周运动中改变运动方向而受到的力。向心力指向圆心或旋转轴。地球上的向心力指向地轴,地面的物体受到的万有引力,可以提供重力和向心力。在极点不受到向心力,所以同一个物体,在极点的重力最大,在赤道的重力最小(但其质量不变)。
25.摩擦力:阻碍物体相对运动(或相对运动趋势)的力叫做摩擦力。如果两个物体接触面粗糙,互相又有压力,还有相对运动趋势,才有摩擦力。压力越大,表面越粗糙,摩擦力越大。放在地面上的物体,未推动和推动的临界点,摩擦力等于推力,一旦推动,摩擦力的大小固定,为压力乘以摩擦系数,与推力无关。
26.杠杆:物理中把一根在力的作用下可绕固定点转动的硬棒叫做杠杆,硬杆可以是各种形状。杠杆绕着旋转的点是支点,使杠杆转动的力为动力,支点到动力作用线的距离为动力臂,阻碍杠杆转动的力为阻力,支点到阻力作用线的距离为阻力臂(如图)。

杠杆平衡的条件是动力矩=阻力矩,即动力×动力臂=阻力×阻力臂。动力臂>阻力臂的杠杆称为省力杠杆,反之为费力杠杆。费力杠杆可以节省距离,但是省力杠杆费距离。
生活中一些工具为了省力的工具都是省力杠杆,比如钳子、羊角锤、启瓶器、撬杠等;为了省距离的工具都是费力杠杆,如筷子、镊子、鱼竿、起重机等。
轮轴的本质是杠杆,利用力矩相等,改变旋转半径,从而改变力的大小。改锥、方向盘、辘轳、扳手都是轮轴,通过增大了轴的半径达到省力的目的。
27.单摆:由轻质杆或细线连接的小球悬于一点,产生往复摆动的装置。摆动的周期与摆的长度负相关。
摆动平面一般认为固定不动。法国物理学家傅科在观察单摆时发现摆动平面在缓慢发生转动,并因此证明了地球的自转。
科学百词
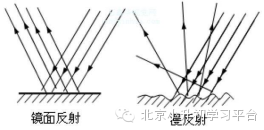
1.镜面反射、漫反射:声波、光波或其他电磁波遇到介质分界面而仍然在原物质中传播的性质称为反射。波的入射角等于反射角(光线与法线的夹角),能量有所消耗。
当反射面光滑时,平行光射到反射面后,仍平行地向另一个方向反射,称为镜面反射。漫反射即不光滑表面使得反射光向各个方向反射。物体正是因为存在漫反射,所以能在各个方向看到其反射的光。(如图)
2.折射:当光从一种介质进入另一种介质时,传播方向发生变化,变化的角度取决于折射率。从空气进入水或玻璃,折射角小于入射角,这是由于水和玻璃的折射率比空气大。同样地,由于光路可逆,从水或玻璃进入空气,反射角小于折射角。空气的折射率比真
空略大一点,太阳光射入大气时也发生了弯折。玻璃棒一半放入水中,在分界面上出现“折断”的现象,就是玻璃棒的光进入人眼时,在水中和空气中路径不同的原因。
3.凸透镜、凹透镜:两个凸出表面组成的透镜叫做凸透镜。平行光射入凸透镜,会经过折射而汇聚到一点,这个点叫做凸透镜的焦距。放大镜和老花镜都是凸透镜,在北极用来聚光取火的冰镜也是凸透镜。
两个凹面组成的透镜叫做凹透镜。平行光射入凹透镜,会发生发散。近视镜就是凹透镜。
4.全反射:光从折射率大的介质射入折射率小的介质(如从玻璃或水中射入空气),当入射角过大时,会发生折射角可能大于 90°的情况,此时所有光线完全发生反射,不发生折射。光纤就是根据这个原理设计的,光在玻璃纤维内部反射,不会射出光纤。海市蜃楼的也是景物反射的光在低空潮湿空气中向高空空气照射过程中发生了很多次全反射造成的(如图)。

5.色散:白光由多种频率的光组成,不同频率的光的折射率不同,因此在被三棱镜两次折射后,路径也不同,不同的光照向了不同位置,出现了从红到紫的光带。彩虹就是空气中的小水滴对光进行折射色散而造成的。肥皂泡上出现的七彩纹路,是由于肥皂泡薄厚不均匀,光发生薄膜干涉的缘故,不属于色散。
6.静电:静电是出于静止状态的电荷。带有静电的物体具有吸引轻小物体的性质。物体通过摩擦失去或得到电子,可以带正电荷或负电荷,当带正电的物体和带负电的物体距离
较近时,会发生放电现象,电荷击穿空气使得正负中和。冬天穿毛衣时经常感觉到“被电”,就是静电的放电现象。雷电也是这种放电现象,雷电的电压和电流都相当巨大,所以高大的建筑物需要安装避雷针,将雷电直接引入大地,防止对人和财产造成伤害。
7.电源:能够提供电流的装置。电源可以把其他形式的能量变成电能,比如电池把内部化学物质的化学能转变为电能,火力发电机是把热能转变为电能,风力发电机、水力发电机亦是如此。
8.电压:电压是电路中能够形成电流的原因,用字母 U 表示。电压值的单位为伏特 V。电流总是从电压高的地方流向电压低的地方。生活中最常见的干电池,正极和负极之间的电压差是 1.5V。生活用电的有效电压值是 220V。
9.电阻:导体对电流阻碍的大小,用字母 R 来表示。电阻值的单位为欧姆Ω。电阻是导体本身的性质,取决于材质、横截面积和长度等。
10.电流:电路中电荷定向移动形成电流,用字母 I 来表示。电流值的单位为安培 A。电流方向是正电荷的移动方向。导线中电子移动的反方向是电流方向。一般来说,导通的回路才可以有电流流过,电流可以转化成其他形式的能量,比如电机做功,灯泡发光,电磁炉发热等。电流的大小取决于电压和电阻,电流与电压大小成正比,与电阻大小成反比。
11.串联、并联:导体头尾相接连在电路中,称为串联(如图)。串联电路中,每个电阻电流相同,电压与电阻成正比。并联电路中,每个电阻两端电压相同,电流与电阻成反比。

12.导体、绝缘体、半导体:可以导电的物体。包括金属、石墨、电解质溶液等。大地和水(非纯净水)是导体。绝缘体是不可以导电的物体,包括一般的塑料、橡胶、陶瓷、纤维等。空气是绝缘体。导体的电阻率很小,绝缘体的电阻率很大,处于二者之间的是半导体,如二极管和电路板等就是用半导体制成的。
导体本身有一定的电阻,不同材料的物体导电性能不一样,现代物理学研究发现,当温度降低到一定程度时,导体会出现对电流的“零阻碍”,也就是电阻为零的情况,称为超导现象。
13.直流电、交流电:直流电拥有稳定的正极和负极,电流流动方向永远不变。干电池就是直流电电源。交流发电电路中,没有固定的正负极,即一个电极为参考电压,另一个电极的电压与之的差值,随着时间呈现周期变化,从正到负再到正。两极之间的电流流动方向也随之变化。生活用电即为频率 50Hz 的交流电,家庭电路的有效电压为 220V,工业电路的有效电压为 380V。三孔插座上,左为零线插孔,右为火线插孔,中间一个为地线,即将用电器的金属外壳接地做保护,防止人触电或机器损毁。



全部 0条评论